The Original Bloom's Taxonomy
Bloom's Taxonomy was created by Dr. Benjamin Bloom in 1956 to promote higher forms of thinking in education. Bloom's Taxonomy is a hierarchical model that categorized learning objectives into varying levels of complexity, from basic to advance knowledge.
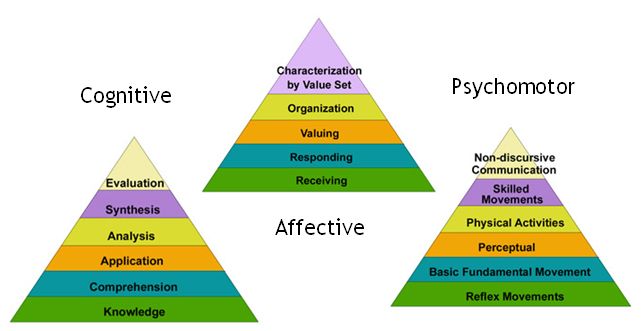
Bloom Taxonomy identified three learning domains, they are; cognitive, affective and psychomotor.
- Cognitive Domain; It focuses on the acquisition and application of knowledge and used in educational setting. There are six major categories of cognitive; knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation. This can be thought as the degree of difficulties. The first one must be mastered before the next one can take place.
- Affective Domain; The affective model came as an extension of Bloom's original work. This domain focuses on how we handle emotions, feelings, values, appreciation, enthusiasm, motivations and attitudes. There are five categories; receiving, responding, valuing, organisation and characterised by value set.
- Psychomotor Domain; This model focuses on the physical movements, coordination and anything related to motor skills. There are 6 categories; reflex movements, basic fundamental movement, perceptual, physical activities, skilled movements and non-discursive communication.
Bloom's Taxonomy Revision
In 2001, the original cognitive model was modified by educational psychologist David Karthwol (was worked with Bloom) and Lorin Anderson (was Bloom's previous student). The new taxonomy reflects more active form of thinking and also include another level of knowledge, which is metacognitive.
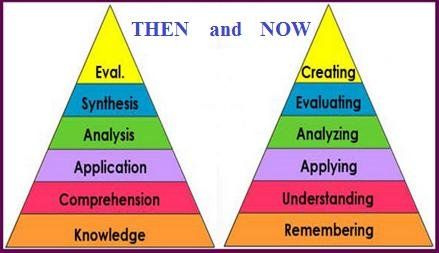
Level 1: Knowledge; This is the basic level. It is related to the memory on what the students have learnt in class. It is an ability to remember knowledge from memory. This is Lower Order Thinking Skills (LOTS)
Level 2: Understanding; This also part of LOTS, It is an ability to construct meaning. The students demonstrate understanding of the knowledge they remembered.









